Overall objective
To provide RTW stakeholders with a definition and framework that promotes understanding of work disability
and the adoption of a common language. This will allow the identification of the stakeholders who play a role in the intervention
process as well as fostering communication between the stakeholders and with the worker.
Elements of methodology
The content is primarily from Lederer, Loisel, Rivard, and Champagne, 2014. We adapted the texts to create a summary version and a full version.
Limitations associated with this content
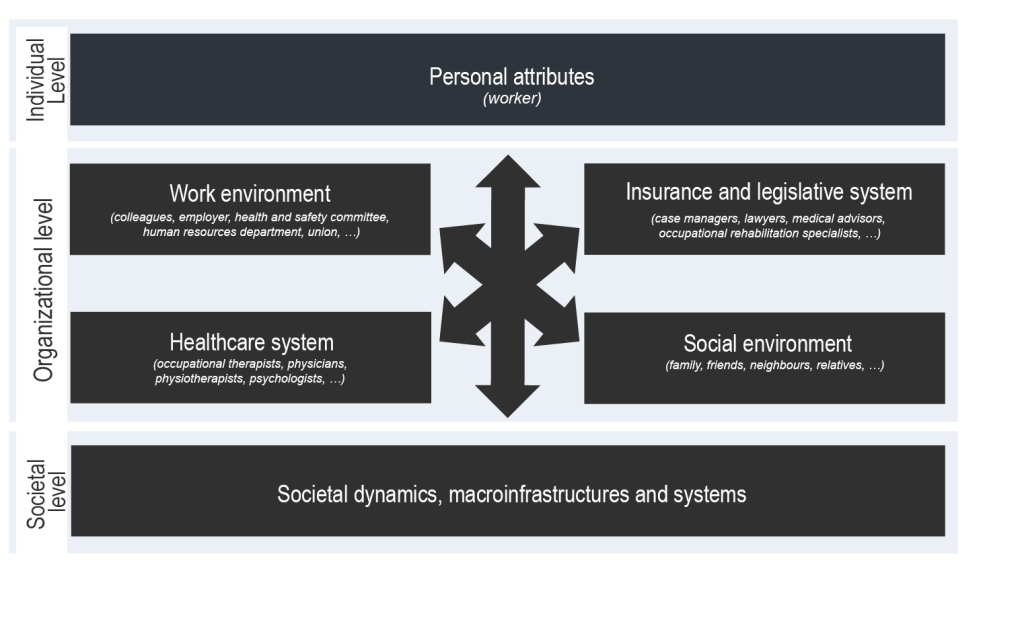
There is no framework (or theoretical model) that considers the perspectives of all RTW stakeholders, much less describes the nature and strength of the interactions between the different risk factors (environmental and personal) and work functioning. We have therefore chosen to present a framework that identifies the forces at play, without illustrating the relationships between these forces.